

Function of the GATA-2 Transcription Factor and the Mechanism Regulating its Expression
|What is the role of GATA-2 in hematopoiesis?
@GATA-2 is one of the transcription factors that contribute to hematopoiesis. Figure 1 shows the differentiation of hematopoietic cells and the transcription factors responsible for each step (gene targeting strategies elucidated the key steps regulated by each factor, as depicted by bars in Figure 1).

Fig. 1. Differentiation of hematopoietic cells. HSC, hematopoietic stem cell; RBC, red blood cell; MgK, megakaryocyte; Plt, paplatelet.
@All GATA transcription factors possess two zinc fingers. They recognize and bind to the DNA sequence "WGATAR". Among the GATA factors, GATA-2 contributes especially to the proliferation and maintenance of hematopoietic stem cells, although the expression of GATA-2 is not limited to hematopoietic tissue and is found in various organs during development. We are interested in how GATA-2 functions in the development of hematopoiesis.
|What is the contribution of GATA-2 to hematopoiesis?
@GATA-2 defective mice die at embryonic day 11.5 due to abnormal hematopoiesis. In GATA-2-null ES cells, the total number of hematopoietic cells following induced cell differentiation was lower than that in wild type ES cells. However, various hematopoietic cells, except mast cells, developed in both GATA-2-null. This suggests the involvement of GATA-2 in cell maintenance and proliferation rather than in differentiation. The precise function of GATA-2 in hematopoiesis is not known. D
|What is our major interest in GATA-2?
@Knowledge gained from mouse analyses has led to advances in human biology and can be applied to clinical medicine. Transgenic mice and gene targeting mice, developed using genetic engineering, have proved useful for analyzing the role of GATA-2 in hematopoietic tissue development.
P@What is the role of GATA-2 in the maintenance and proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells?
@We previously reported that the gene structure of GATA-2 has two alternative first exons, giving rise to two alternative mRNA sequences. In these two exons, IS (first specific) and IG (first general), the IS exon is specifically expressed in hematopoietic tissues. We made a knock-in mouse with GFP cDNA in the locus of the IS exon. In these mice, hematopoietic cells express the GFP protein in accordance with GATA-2 expression, especially with transcription of the IS exon. We are characterizing hematopoietic cells from the fetal liver or bone marrow derived from these mice.
Q@Which signals direct GATA-2 expression in hematopoietic stem cells?
@We constructed the reporter plasmid 7.0ISGFP by fusing 7.0 kb of the 5' flanking sequence of the IS exon with a GFP reporter gene. GFP is expressed in the hematopoietic tissues of transgenic mice bearing this construct. We made several deleted or mutated constructs of the 7.0 kb 5' flanking sequence. As long as the limited regulatory regions contain the hematopoietic enhancer, transgenic mice continue to express GFP protein specifically in hematopoietic tissue. Figure 2 shows the transgenic mouse embryos at E9.5 carrying one such construct.
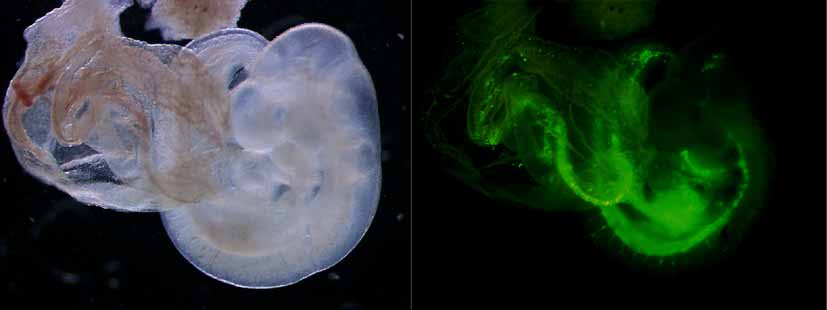
Fig. 2. Transgenic mouse embryos. Left, bright field; right, fluorescent microscopic photograph.
@Combination of the results obtained using several constructs may elucidate the minimal essential element required. This sequence is expected to be rather shorter than 7.0 kb and, if for example, it is defined as around 20 bp sequence, the transcription factor which binds to it should be easily identified. These analyses should solve the signaling mechanism regulating GATA-2 expression and, furthermore, the molecular mechanism controlling hematopoietic development.
REFERENCE